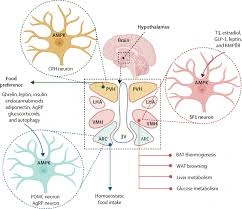
Ketogenic Diet
Introduction
In traditional medicine, the ketogenic diet—a high-fat, adequate-protein, low-carb diet—is mostly used to treat children with refractory epilepsy, or epilepsy that is difficult to control. Instead of burning carbs, the diet makes the body burn fat.
The ketogenic diet calls for ingesting very few carbohydrates and substituting them with fat to assist your body in burning fat for energy. Two health benefits of this diet are losing weight and reducing your risk of developing certain diseases.
A ketogenic diet is based on eating foods that are high in fat and low in carbohydrates. Various animal proteins, dairy products, vegetables, various plant-based foods, and fats and oils can all be consumed by those who follow this diet.
The ketogenic diet, sometimes known as the “keto diet,” is a high-fat, low-carb diet with numerous health advantages. This diet can help you lose weight and improve your health, according to numerous research.
Even diabetes, cancer, epilepsy, and Alzheimer’s disease may be prevented by following a ketogenic diet.
For some people who have struggled to lose weight using traditional approaches, a ketogenic diet can be an alternative. Each person’s genetic mix and body composition will determine the precise proportion of fat, carbohydrate, and protein required to attain health advantages.
A doctor and dietitian should therefore be consulted if one decides to begin a ketogenic diet to closely monitor any biochemical changes that may occur after beginning the regimen, to develop a meal plan that is specific to one’s current medical conditions, and to avoid nutritional deficiencies or other health issues. This is a thorough introduction to the ketogenic diet.
On the ketogenic diet, what do I eat?
What you eat depends on the sort of ketogenic diet, which comes in a variety of forms.
- The standard ketogenic diet (SKD) is characterized by a high-fat, moderate-protein, and extremely low-carb diet. Usually, it has only 10% carbohydrates, 20% protein, and 70% fat.
- The cyclical ketogenic diet (CKD) alternates periods of higher-carbohydrate refeeds, for example, two high-carb days after five ketogenic days.
- Targeted ketogenic diet (TKD), you can incorporate carbohydrates into your diet in between workouts.
Similar to a regular ketogenic diet, but with additional protein, is the high-protein ketogenic diet. Typically, the proportion is 35% protein, 5% carbohydrates, and 60% fat.
Only the conventional and high-protein ketogenic diets, nevertheless, have been thoroughly researched. Athletes and bodybuilders are the main users of more sophisticated cyclical or targeted ketogenic diets.
Although many of the same concepts also apply to the other variations, the majority of the information in this article is relevant to the standard ketogenic diet (SKD).
What is ketosis?
A low-carb diet, such as the Atkins diet, is referred to as “ketogenic.” The goal is to consume fewer calories from carbs and more calories from fat and protein. The carbohydrates that are easiest to digest, such as sugar, soda, white bread, and pastries, are the ones you reduce the most.
In the metabolic condition known as ketosis, your body burns fat for energy rather than carbohydrates.
It happens when you drastically cut back on the amount of carbs you eat, which limits the amount of glucose (sugar), the primary energy source for cells.
The best approach to go into ketosis is to follow a ketogenic diet. This usually entails consuming no more than 20 to 50 grams of carbohydrates per day and consuming a lot of fats from foods like meat, fish, eggs, nuts, and healthy oils.
It’s also critical to consume protein in moderation. This is because consuming large amounts of protein can cause it to be turned into glucose, which could delay your entry into ketosis.
Intermittent fasting may also facilitate a quicker transition into ketosis. Although there are other variations of intermittent fasting, the most popular approach entails cutting back on food consumption to about eight hours each day and fasting for the remaining sixteen.
There are tests for blood, urine, and breath that measure the quantity of ketones your body produces and can help you identify if you’ve entered ketosis.
You may also be in ketosis if you experience certain symptoms, such as increased thirst, dry mouth, frequent urination, and decreased appetite or hunger.
The ketogenic diet is a way of eating that emphasizes foods that are high in good fats, low in carbohydrates, and high in protein. Getting more calories from fat than from carbohydrates is the aim.
Depleting the body’s sugar stores is how the diet works. It will then begin converting fat into energy. As a result, the body produces molecules known as ketones, which it uses as fuel. Weight loss might also result from the body burning fat.
The Standard Keto Diet and the Cyclical Keto Diet are two of the various varieties of the ketogenic diet. The advantages and disadvantages of the ketogenic diet are discussed in this article.
Can I lose weight on the ketogenic diet?

Losing weight and reducing illness risk factors are two benefits of a ketogenic diet. According to research, the ketogenic diet might help people lose weight just as well as a low-fat diet.
Additionally, the diet is so satisfying that you can lose weight without keeping track of your food consumption or calorie intake.
A very low-carb, ketogenic diet was marginally more beneficial than a low-fat diet for long-term weight loss, according to an assessment of 13 research. On average, those who adhered to the ketogenic diet dropped two pounds (0.9 kg) more than those who followed a low-fat diet.
Additionally, it resulted in decreases in lipid levels and diastolic blood pressure.
Thirty-four older persons who followed a ketogenic diet for eight weeks lost almost five times as much total body fat as those who followed a low-fat diet, according to another study.
A significant part might also be played by the elevated ketones, decreased blood sugar, and enhanced insulin sensitivity. Read this article to learn more about how a ketogenic diet affects weight reduction.
Can individuals with diabetes and prediabetes benefit from the ketogenic diet?
- Changes in metabolism, elevated blood sugar, and compromised insulin activity are the hallmarks of diabetes.
- Type 2 diabetes, prediabetes, and metabolic syndrome are all closely associated with excess fat, which can be lost with the ketogenic diet.
- According to a previous study, the ketogenic diet increased insulin sensitivity by an astounding 75%.
In addition, a 90-day ketogenic diet dramatically lowered hemoglobin A1C levels, a gauge of long-term blood sugar control, in a small study of women with type 2 diabetes.
In a different study, 349 individuals with type 2 diabetes who were on a ketogenic diet lost an average of 26.2 pounds (11.9 kg) during two years. Given the connection between type 2 diabetes and weight, this is a significant advantage.
Additionally, during the course of the trial, participants’ use of certain blood sugar drugs dropped, and they also had better blood sugar management.
See this article on the advantages of low-carb diets for diabetics for additional details.
The ketogenic diet was first developed as a treatment for neurological conditions like epilepsy. Recent research has demonstrated that the diet can help with a wide range of illnesses.
Who Makes Use of It?
The most common reason people follow a ketogenic diet is to reduce weight, but it can also help treat medical disorders like epilepsy. Although more research is needed in certain areas, it may also assist those with heart disease, some brain ailments, and even acne. To find out if a ketogenic diet is healthy for you, especially if you have type 1 diabetes, consult your doctor first.
Encourages weight loss
Increasing metabolism and decreasing appetite are two ways that the ketogenic diet may aid in weight loss.
Foods that fill one up and may lower hunger-stimulating hormones are part of ketogenic diets. These factors suggest that a ketogenic diet may decrease appetite and encourage weight loss.
Researchers discovered that over the course of a year, those who followed ketogenic diets lost two pounds (lbs) more than those who followed low-fat diets in a 2013 meta-analysis of thirteen separate randomized controlled studies.
Cancer
Your body may use or store sugar as fuel thanks to the hormone insulin. You don’t need to store this fuel because ketogenic diets cause you to burn through it quickly. This implies that your body produces less insulin and requires less of it. The growth of cancer cells may be slowed or you may be protected against some types of cancer by such reduced levels. However, this requires further investigation.
Heart Conditions
Although it may seem odd, ketogenic diets are associated with both a decrease in “bad” cholesterol and an increase in “good” cholesterol. The reason for this could be that these diets prevent your body from producing more cholesterol by lowering insulin levels. This implies that you have a lower risk of heart failure, high blood pressure, hardened arteries, and other cardiac disorders. However, the duration of these effects is unknown.
Acne
Reducing carbohydrates may assist because they have been connected to this skin issue. Additionally, a ketogenic diet may help prevent acne by causing a decrease in insulin. (Your body may produce other hormones that trigger outbreaks as a result of insulin.) To find out just how much, if any, of an impact the food has on acne, further research is still required.
There are several causes for acne, and in certain cases, blood sugar and food may be related.
Consuming a lot of processed and refined carbs can negatively impact skin health by changing the balance of gut bacteria and causing blood sugar levels to fluctuate dramatically.
A 2012 study found that a ketogenic diet may help some persons with acne by lowering their carbohydrate intake. Go here to learn more about acne.
Diabetes

Compared to other diets, low-carb diets appear to help maintain lower and more consistent blood sugar levels. However, your body produces substances known as ketones when it consumes fat for energy. An excessive amount of ketones in the blood can be harmful to those with diabetes, especially type 1. Therefore, it’s crucial to discuss any dietary modifications with your doctor.
Having epilepsy
Since the 1920s, ketogenic diets have been employed to assist manage seizures brought on by this illness. But once more, it’s critical to collaborate with your physician to determine what’s best for you or your child.
A ketogenic diet’s proportions of fat, protein, and carbohydrates change how the body uses energy, which leads to ketosis. The body uses ketone bodies as fuel during the metabolic process known as ketosis.
According to the Epilepsy Foundation, individuals with epilepsy who have not responded to various forms of treatment may experience fewer seizures when they are in ketosis. Although it appears to have the most impact on children with focal seizures, more research is required to determine its effectiveness.
Other Conditions of the Nervous System
These have an impact on your spine, brain, and the nerves that connect them. In addition to epilepsy, a ketogenic diet may also help with Parkinson’s disease, Alzheimer’s disease, and sleep difficulties. Although the exact cause is unknown, the ketones your body produces as they burn fat for energy may shield your brain cells from harm.
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
This occurs when a woman’s ovaries enlarge beyond their normal size and tiny sacs packed with fluid surround the eggs. It can be brought on by high insulin levels. Together with other lifestyle modifications like exercise and weight loss, ketogenic diets may help treat it because they reduce the amount of insulin your body produces as well as the quantity you need.
Work out
For example, endurance athletes like cyclists and runners may benefit from a ketogenic diet throughout their training. Over time, it improves your body’s ability to use oxygen when working hard and increases your muscle-to-fat ratio. However, it might not be as effective as other diets for achieving peak performance, even though it might help with training.
Adverse Reactions
The more prevalent ones are typically not serious: You may have indigestion, slight hypoglycemia, or constipation. Low-carb diets are much less likely to cause kidney stones or acidosis, which is an excess of acid in the body. The “keto flu,” which can include headache, weakness, and irritability, as well as weariness and poor breath, are possible additional adverse effects.
Eat Carefully
Your kidneys may suffer as your body burns up its fat reserves. Additionally, if you are fat due to other health conditions you are likely to have, such as diabetes, a heart ailment, or high blood pressure, it may be difficult to start a ketogenic diet or return to a regular diet later. Make dietary adjustments gradually and only under your doctor’s supervision if you suffer from any of these conditions.
How It Operates
Your body eventually runs out of quick-use fuel (blood sugar) when you consume less than 50 grams of carbohydrates each day. Usually, this takes three to four days. After that, you’ll begin to use fat and protein as fuel, which may help you lose weight. We refer to this as ketosis. It’s crucial to remember that the ketogenic diet is a temporary eating plan that prioritizes weight loss over the search for health advantages.
On a ketogenic diet, what foods should I avoid?
Limit your intake of any foods heavy in carbohydrates. The following foods must be cut back on or avoided when following a ketogenic diet:
- Sweet foods, such as fruit juice, soda, smoothies, cakes, candies, and ice cream.
- Starches or grains: cereal, rice, pasta, wheat-based goods, etc.
- Fruit: every fruit, except tiny amounts of berries, such as strawberries
- Legumes, or beans, such as kidney beans, chickpeas, lentils, and peas.
- Potatoes, sweet potatoes, carrots, which are parsnips, and other root vegetables and tubers.
- Low-fat or diet items: salad dressings, condiments, and low-fat mayonnaise
- Some sauces or condiments, such as ketchup, teriyaki sauce, honey mustard, and barbecue sauce.
- Harmful fats, such as mayonnaise and processed vegetable oils.
- Alcohol: mixed beverages, wine, beer, and liquor
- Sugar-free sugar-free diet items, such as syrups, puddings, sweets, sweeteners, and desserts.
On the ketogenic diet, what foods may I eat?

Followers of the ketogenic diet are required to consume fat at every meal due to the diet’s high-fat requirements. That might be equivalent to 165 grams of fat, 40 grams of carbohydrates, and 75 grams of protein per day on a diet of 2,000 calories. However, your specific needs will determine the precise ratio.
The ketogenic diet permits the use of certain healthful unsaturated fats, such as those found in avocados, tofu, nuts (walnuts, almonds), seeds, and olive oil. However, high intakes of saturated fats from butter, cocoa butter, lard, and oils (palm and coconut) are recommended.
The ketogenic diet includes protein, but it usually doesn’t distinguish between meals that are high in lean protein and those that are high in saturated fat, such as bacon, pig, and cattle.
How about veggies and fruits?
Although all fruits are high in carbohydrates, you can consume small amounts of some fruits, most commonly berries. Only leafy greens (kale, spinach, Swiss chard, etc.), cauliflower, broccoli, Brussels sprouts, asparagus, bell peppers, onions, garlic, mushrooms, cucumber, celery, and summer squashes are considered vegetables (also high in carbohydrates). There are roughly six carbohydrates in a cup of chopped broccoli.
These foods should serve as the foundation for most of your meals:
- Meat, including bacon, chicken, turkey, ham, sausage, steak, and red meat.
- Fatty fish include mackerel, salmon, trout, and tuna.
- Omega-3 whole eggs or pastured eggs
- Grass-fed butter and heavy cream cheese: raw cheeses such as blue, mozzarella, goat, cheddar, or cream
- Almonds, walnuts, flaxseeds, pumpkin seeds, chia seeds, and so forth.
- Healthy oils include avocado oil and extra virgin olive oil.
- Avocados: entire avocados or freshly prepared guacamole Low-carb vegetables: peppers, tomatoes, onions, and green vegetables, among others.
- Condiments: spices, herbs, salt, and pepper
Your diet should mostly consist of whole foods made with only one component. This is a list of 44 low-carb, healthful foods.
A one-week keto meal plan example
Here is an example one-week ketogenic diet meal plan to get you started: Vegetable and egg muffins with tomatoes for breakfast
Monday
- Lunch consists of feta cheese, olives, olive oil, and chicken salad with a side salad.
- The supper will be fish and butter-cooked asparagus.
Tuesday
- Breakfast consists of spinach, tomato, egg, and basil. Almond milk, spinach, peanut butter, cocoa powder, and stevia milkshake for an omelet meal accompanied by sliced strawberries.
- Dinner will be salsa and cheese-shell tacos.
Wednesday
- Breakfast is blackberry and coconut-topped nut milk chia pudding.
- Lunch is shrimp salad with avocado.
- Dinner will be vegetables, salad, and pork chops with Parmesan cheese.
Thursday
- Breakfast consists of an omelet topped with salsa, avocado, peppers, onions, and spices.
- Lunch would be guacamole and salsa with celery sticks and a handful of almonds.
- Dinner will be grilled zucchini on the side and chicken filled with pesto and cream cheese.
Friday
- Breakfast consists of fruit, peanut butter, chocolate powder, and sugar-free Greek whole milk yogurt.
- Lunch would be lettuce wrap tacos with ground meat and bell pepper slices.
- The supper will be mixed vegetables and loaded cauliflower.
Saturday
- Cream cheese pancakes with blueberries and grilled mushroom
- Lunch would be a “noodle” salad of zucchini and beets; dinner would be white fish grilled in olive oil with kale and toasted pine nuts.
Sunday
- Breakfast consists of fried eggs and mushrooms.
- Low-carb broccoli and sesame chicken for lunch; spaghetti squash for supper The Bolognese
- Since each variety of meat and vegetables offers unique nutrients and health advantages, it is always best to try to rotate them over time.
Check out this keto shopping list and these 101 healthful low-carb recipes for a ton of meals.
Nutritious keto snacks
Here are some nutritious, keto-approved snacks to have on hand in case you become hungry in between meals:
- Fish cheese or fatty meat
- An assortment of seeds or nuts
- Bits of keto sushi with olives
- Deviled or hard-boiled eggs, one or two.
- Keto-friendly snack bars
- 90% dark chocolate, full-fat Greek yogurt, cocoa powder, and nut butter
- The guacamole with bell peppers
- Plain cottage cheese and strawberries
- smaller servings of leftover food, such as beef jerky with salsa guacamole and celery
- Bombs of fat
Keto advice and techniques
Although beginning the ketogenic diet can be difficult, there are a few strategies you can employ to make it simpler.
- To find out how your favorite foods can fit into your diet, start by being familiar with food labels and looking at the grams of fat, carbohydrates, and fiber.
- Another advantage of meal planning is that it can help you save more time over the week.
- You can create your menu by using the keto-friendly recipes and meal ideas found on a lot of websites, food blogs, apps, and cookbooks.
- For a quick and easy way to eat keto meals at home, some meal delivery services even provide keto-friendly selections.
- When you’re pressed for time, consider ordering nutritious frozen keto meals.
- You might also want to think about carrying your own food when you’re going to social events or visiting family and friends. This can help you avoid cravings and keep to your meal plan.
Advice for ketogenic diet eaters
You can make a lot of restaurant dishes keto-friendly. The majority of eateries serve some form of seafood or meat-based dish. Get this and swap out any high-carbohydrate foods for more veggies.
Egg-based dishes, such as eggs with bacon or an omelet, are also excellent choices. Burgers without buns are also a favorite. Vegetables could be used in place of the fries. Add more eggs, bacon, cheese, or avocado.
Any kind of meat is served with extra cheese, guacamole, salsa, and sour cream at Mexican restaurants. Request a mixed cheese platter or berries and cream for dessert.
Side effects
While most healthy people can safely follow the ketogenic diet, there may be some initial adverse effects as your body adjusts.
These consequences, sometimes known as the “keto flu,” have been anecdotally documented. Some people on the eating plan have reported that it normally ends in a few days.
Constipation, vomiting, and diarrhea are among the symptoms of the keto flu that have been reported. Other, less typical symptoms consist of:
- Low vitality and cognitive abilities
- Increased hunger and problems with sleep
- Reduced workout performance due to nausea and intestinal discomfort
For the first few weeks, you can follow a standard low-carb diet to reduce this. Before you stop eating carbohydrates altogether, this might train your body to burn more fat.
Adding salt to your food or taking mineral supplements may assist because a ketogenic diet can also alter your body’s water and mineral balance. Discuss your dietary requirements with your physician.
Eat till you’re satisfied and refrain from severely limiting your caloric intake, at least initially. A ketogenic diet typically results in weight loss without deliberate calorie limitation.
Are there hazards associated with following the ketogenic diet?
Although there are advantages to the ketogenic diet, maintaining it for an extended period may have certain drawbacks, such as the following risks:
- Low blood protein, excess liver fat, and renal stones
- Deficits in micronutrients
- Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors are a class of medicine used to treat type 2 diabetes that can raise the risk of diabetic ketoacidosis, a hazardous condition that causes blood acidity to rise. The ketogenic diet should be avoided by anyone using this drug.
The long-term safety of the ketogenic diet is being investigated further. To help you make decisions, keep your doctor updated on your diet.
Does the ketogenic diet have any supplements?
Supplements are not necessary, although they can be helpful.
- MCT oil. MCT oil, when added to beverages or yogurt, boosts ketone levels and gives you energy. Purchase MCT oil on the internet.
- Minerals. Due to changes in the water and mineral balance, more salt and other minerals may be crucial when beginning.
- Caffeine. Caffeine can improve performance, energy, and fat reduction.
- Exogenous ketones. The body’s ketone levels may be raised by this supplement.
- Creatine. There are several health and performance advantages to creatine. If you are combining exercise and a ketogenic diet, this may be beneficial.
- Whey. To boost your daily protein consumption, add half a scoop of whey protein to smoothies or yogurt. Purchase delicious whey products online.
Risks of a ketogenic diet
The hazards of a ketogenic diet are numerous. First and foremost, it contains a lot of saturated fat. Because saturated fats are linked to heart disease, McManus advises consuming no more than 7% of your daily calories from them. The ketogenic diet indeed raises harmful LDL cholesterol, which is connected to heart disease.
The following are other possible keto risks:
- Lack of certain nutrients. According to McManus, you run the danger of experiencing shortages in micronutrients such as selenium, magnesium, phosphorus, and vitamins B and C if you don’t eat a diverse range of fruits, vegetables, and grains.
- Issues with the liver. The diet may exacerbate any pre-existing liver issues because there is so much fat to process.
- Kidney issues. According to McManus, the ketogenic diet may overburden the kidneys, which aid in the metabolism of protein. As of right now, women should consume 46 grams of protein daily on average, while males should consume 56 grams.
- Constipation. Legumes and grains are examples of fibrous foods that are low in the ketogenic diet.
- Mood swings and fuzzy reasoning. When the brain is powered by sugar from nutritious carbs, it functions at its peak efficiency. Diets low in carbohydrates can make people confused and irritable.
Before beginning a ketogenic diet, see a physician and a trained dietitian because those dangers might mount up.
Complication
There could be several health advantages to the ketogenic diet. Long-term use of the ketogenic diet, however, may have negative health effects, such as an elevated risk of the following conditions:
Renal stones, high blood protein, vitamin and mineral deficits, and hepatic fat accumulation Many individuals refer to the negative side effects of the ketogenic diet as “keto flu.” These negative consequences could consist of:
- Tiredness, low blood sugar, and constipation
- Headaches, nausea, vomiting, and a limited tolerance for physical activity
- At the start of the diet, while the body is getting used to its new energy source, these symptoms are particularly prevalent.
The following groups should not follow the ketogenic diet:
Individuals with diabetes who require insulin, those with eating problems, those with kidney illness, or women who are pregnant or nursing
A ketogenic diet is also not recommended for those with type 2 diabetes who are on sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors. This drug raises the risk of diabetic ketoacidosis, a serious illness that causes blood acidity to rise.
Learn more about why following a ketogenic diet may not result in weight loss.
This low-carb, high-fat diet may also aid in the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease, some types of cancer, and other illnesses, according to preliminary data. However, more thorough research is still required to ascertain the long-term safety and efficacy of the ketogenic diet.
Typically, the ketogenic diet restricts daily carbohydrate intake to 20–50 grams.
Some ketogenic individuals track their overall carbohydrate intake, while others track their net carbohydrate intake. Total carbs less fiber is referred to as net carbs. This is due to the fact that fiber is indigestible, meaning your body cannot break it down and absorb it.
Despite its seeming difficulty, this diet enables its adherents to consume a wide variety of nutrient-dense foods.
These are twenty nutritious ketogenic foods.
Seafood
Shellfish and fish are excellent keto-friendly foods. In addition to being almost carb-free, salmon and other fish are high in potassium, selenium, and B vitamins.
However, each variety of shellfish has a different carbohydrate content. Oysters and octopuses have carbohydrates, however, shrimp and the majority of crabs do not. These items are still acceptable on the ketogenic diet, but you must closely monitor your carb intake to keep it within acceptable limits.
Furthermore, omega-3 fats, which are abundant in salmon, sardines, mackerel, and other fatty fish, have been linked to decreased insulin levels and improved insulin sensitivity in overweight and obese individuals.
Regular consumption of fish is associated with better brain function and a lower risk of illness. 8 to 10 ounces of seafood should be consumed weekly by adults over the age of 18, according to the American Heart Association.
Poultry and meat
On the ketogenic diet, meat and poultry are regarded as staple foods.
In addition to being low in carbohydrates, fresh meat and poultry are high in B vitamins and other vital elements. Additionally, they are a fantastic source of high-quality protein, which could assist maintain muscle mass when following a very low-carb diet.
A diet rich in fatty meat raised HDL (good) cholesterol levels by 8% compared to a diet low in fat and high in carbohydrates, according to a small study conducted on older women.
Since grass-fed beef contains more omega-3 fats and conjugated linoleic acid (CLA) than meat from animals fed grain, it could be preferable to choose it if at all possible.
Eggs
One of the healthiest protein sources is eggs.
Eggs can be perfect for keto because each large egg has roughly 6 grams of protein and less than 1 gram of carbohydrates. Eggs have also been demonstrated to release chemicals that heighten sensations of fullness.
Since the yolk of an egg contains the majority of its nutrients, it is crucial to consume whole eggs rather than egg whites. This includes the eye-health-promoting antioxidants zeaxanthin and lutein.
Despite having a high cholesterol content, egg yolks don’t seem to raise your risk of heart disease.
Cheese
Cheese comes in hundreds of varieties, and the majority of them are excellent for the ketogenic diet since they are high in fat and very low in carbohydrates.
One gram of carbohydrates, six grams of protein, and a healthy dose of calcium are all found in only one ounce (28 grams) of cheddar cheese.
Despite having a high saturated fat content, cheese has not been linked to an increased risk of heart disease. According to some research, it might offer some protection against this illness.
Additionally, cheese includes CLA, which has been connected to benefits in body composition and fat loss. Regular cheese consumption may also lessen the aging-related loss of strength and muscular mass.
In a 12-week research, older persons who had 7 ounces (210 grams) of ricotta daily lost less muscle mass and strength than those who did not consume this quantity of cheese.
These cheeses are better for a ketogenic diet because they have fewer carbohydrates.
- Blue cheese on the keto cheese list
- Brie Chevre Camembert
- Cream cheese with Colby Jack cottage cheese
- Feta
- Halloumi with goat cheese
- Havarti
- Limburger
- Mascarpone Manchego
- Mozzarella
- Muenster
- Provolone with Parmesan and pepper jack
- String cheese Romano
- Cheese from Switzerland
Cottage cheese and plain Greek yogurt
Cottage cheese and plain Greek yogurt are wholesome, high-protein foods. You can consume them on keto in moderation even if they include some carbohydrates.
Cottage cheese and yogurt have both been demonstrated to support feelings of fullness and reduce hunger.
While each one is a great snack on its own, you can make a quick keto treat by mixing them with chopped almonds, cinnamon, or other spices.
Half-and-half and cream
The fatty part of fresh milk that separates during milk processing is what makes up cream. Conversely, half-and-half is composed of 50% whole milk and 50% cream.
These dairy products are perfect for keto because they are high in fat and very low in carbohydrates.
Butter and cream, like other fatty dairy products, are high in CLA, which may help people lose weight. Nevertheless, it’s preferable to use cream and half-and-half sparingly.
People should restrict foods high in saturated fat, according to the American Heart Association’s 2021 dietary guidelines. A decreased risk of heart disease and stroke is associated with substituting plant-based or polyunsaturated lipids for animal and dairy fats.
According to certain research, there may not be a strong correlation between heart disease and high-fat dairy products. According to some, consuming high-fat dairy products in moderation may lower your risk of heart attack and stroke. But the evidence is still equivocal.
The degree of processing that food has undergone is one of the numerous variables that can influence this topic, which is still up for debate.
Popular options for adding to coffee or using as keto substitutes for tiny amounts of milk in cooking include cream and half-and-half.
Plant-based milk without sugar
Soy, almond, and coconut milk are among the plant-based milk types that are suitable for keto. Choose varieties that aren’t sweetened. Too much sugar makes sweetened choices unsuitable for a ketogenic diet.
Additionally, even unsweetened oat milk has too many carbohydrates to be keto-friendly, so you should stay away from it.
Leafy green vegetables
Green leafy vegetables are great for keto since they are incredibly low in carbohydrates. They are also abundant in antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals.
Iron and vitamin K are especially abundant in dark leafy greens like collard greens, kale, and spinach.
Greens provide your meals with more substance without significantly raising the amount of carbohydrates. Herbs like rosemary and oregano can offer a lot of flavor with virtually no carbohydrates.
- These leafy greens are keto-friendly
- Greens for salads: Friese, escarole, arugula, baby spinach, and lettuce
- Swiss chard, cabbage, book choy, collard greens, mustard greens, kale, and spinach are examples of cooking greens.
- Herbs: lemongrass, basil, dill, parsley, cilantro, thyme, sage, mint, oregano.
Peppers
Several types of peppers are suitable for the ketogenic diet. In cookery, they are treated like vegetables even though they are fruits.
Jalapeños are perfect for keto-friendly appetizers, and small spicy peppers lend a little spiciness to recipes. Larger, milder peppers like bell peppers and poblanos can be stuffed to create tasty low-carb main courses, or they can be used in a variety of recipes.
Vitamin C is also abundant in peppers. For example, 107% of the daily value (DV) of vitamin C is found in one bell pepper.
Summer squash
Summer squashes, like zucchini and yellow squash, are very adaptable and low in carbohydrates.
Zucchini is very popular on the ketogenic diet. You can make zucchini noodles with a spiralizer, which is a great alternative to noodles or spaghetti.
Grated zucchini can be added to baked products without changing the flavor or used as a rice substitute. You may also use a mandoline to thinly slice it, then sprinkle it with salt, pepper, and olive oil to eat as a cold salad.
High-fat vegetables
Although they are both considered fruits, avocados, and olives are different from other vegetables in that they contain a significant amount of fat. They are also low in net carbohydrates and high in fiber. Olives primary antioxidant, oleuropein, has anti-inflammatory qualities and may shield your cells from harm.
Furthermore, one study discovered that eating one avocado daily improved heart health risk factors, such as lower LDL (bad) cholesterol levels.
Additional vegetables that aren’t starchy
Numerous additional non-starchy veggies are rich in minerals and antioxidants yet low in calories and carbohydrates. Additionally, low-carb vegetables are excellent alternatives to high-carb diets.
For example, it’s simple to make low-carb cauliflower into mashed cauliflower or cauliflower rice. Low-carb root vegetables like turnips and jicama are excellent alternatives to roasted potatoes or French fries, while spaghetti squash is a natural spaghetti substitute. Here are a few more veggies that are keto-friendly.
List of ketogenic vegetables:
- Broccoli and asparagus
- Cauliflower with cabbage mushrooms
- Tomatoes, cucumbers, green beans, and eggplant
- Jicama spaghetti squash
- Turnips and radishes
- Brussels sprouts
- Okra and celery
Seeds and nuts
Nuts and seeds are low in carbohydrates, high in fat, and healthy.
- Regular consumption of nuts is associated with a lower risk of depression, heart disease, some types of cancer, and other chronic illnesses.
- Additionally, the high fiber content of nuts and seeds might naturally reduce your caloric intake and help you feel full.
The amount of net carbohydrates in nuts and seeds varies greatly depending on the kind, even though most of them are low. The greatest for keto because they have the fewest carbohydrates are :
- Pecans, macadamia nuts, and almonds
- Chia seeds and walnuts
- Flaxseeds
Berries
On the ketogenic diet berries are an exception to the rule that most fruits are too rich in carbohydrates.
Berries, especially strawberries and raspberries, are high in fiber and low in carbohydrates. Despite having fewer carbohydrates than some other fruits, blueberries, and blackberries might not be suitable for stringent ketogenic diets.
Packed with antioxidants, these little fruits may help prevent disease and lessen inflammation.
Noodles from Shirataki
A great complement to the ketogenic diet are shirataki noodles. Due to their high water content, they only provide 15 calories per serving and less than 1 gram of net carbohydrates. The viscous fiber used to make these noodles, glucomannan, has several possible health advantages.
Food passes more slowly through the digestive tract when viscous fiber gels. By reducing hunger and blood sugar surges, this can help manage diabetes and help people lose weight.
Shirataki noodles are available in a number of shapes, including as linguine, fettuccine, and rice. In nearly every dish, they can be substituted for ordinary noodles.
Cocoa powder and dark chocolate
Antioxidants found in dark chocolate and cocoa are tasty.
Flavanols, which are found in dark chocolate, can lower blood pressure and maintain healthy arteries, perhaps lowering your risk of heart disease.
Surprisingly, chocolate is OK when following a ketogenic diet. But it’s crucial to eat dark chocolate in moderation and to go for one that has at least 70% cocoa solids, ideally more.
Olive oil
Your heart can benefit greatly from olive oil. It contains a lot of oleic acid, a monounsaturated fat that has been shown to lower risk factors for heart disease.
Furthermore, polyphenol antioxidants, which are plant substances that further preserve heart health by reducing inflammation and enhancing arterial function, are abundant in extra-virgin olive oil.
Olive oil has no carbohydrates because it is a pure fat source. It’s the perfect foundation for nutritious mayonnaise and salad dressings.
It’s preferable to cook with olive oil on low heat or add it to food after it’s been cooked because it’s not as stable at high temperatures as saturated fats.
Avocado and coconut oils are also great plant-based oils to explore on keto.
Ghee and butter
When following the ketogenic diet, it’s beneficial to include fats like butter and ghee. Ghee is carb-free, and butter has very little levels of carbohydrates.
When butter is heated and the milk particles that float to the top are removed, ghee is created. It is frequently used in Indian cooking and has a strong buttery flavor.
Butter and ghee, like other forms of full-fat dairy, don’t seem to be as bad for you as people once believed.
Tea and coffee without sugar
Tea and coffee are nutritious, low-carb beverages.
They include caffeine, which speeds up your metabolism and may enhance your mood, alertness, and physical performance.
Additionally, it has been demonstrated that people who drink tea and coffee have a far lower chance of developing diabetes. Although a cause-and-effect relationship has not yet been established, the people who consume the most coffee are the least in danger.
It’s okay to add heavy cream to coffee or tea, but since “light” coffee and tea lattes are usually produced with nonfat milk and high-carb flavorings, you’ll need to stay away from them while on keto.
Sparkling water without sugar
Unsweetened sparkling water is an excellent option if you’re searching for a soda substitute that is keto-friendly.
Although they can be flavored, these wonderfully bubbly drinks typically don’t include any sugar or sweeteners. They don’t contain any calories or carbohydrates because of this.
Some types, on the other hand, may contain carbohydrates since they are naturally flavored with small amounts of fruit juice. Extra carbohydrates can rapidly add up, so be sure to read the label.
The bottom line
Blood sugar regulation, weight loss, and other health objectives may be aided by the ketogenic diet. Its high-fat, low-carb strategy, however, could initially seem unduly restricted.
However, this pattern allows you to stay within your daily carb limit while incorporating a wide selection of pleasant, nutritious, and adaptable meals.
Eating a wide range of these foods is the best way to get the full health benefits of the ketogenic diet. Any planned diet plan should be discussed with a physician, dietician, or other qualified healthcare professional, particularly for those attempting to manage a disease or health issue.
To make sure the keto diet is a safe eating pattern, people who want to begin it should see a doctor and find out whether they have diabetes, hypoglycemia, heart disease, or any other medical concerns.
Remember that there aren’t many studies on the ketogenic diet’s long-term advantages. It’s uncertain if sticking to this diet for longer periods is better than consuming healthier, less restrictive foods.
Carbohydrate intake is significantly limited on a ketogenic diet. Nonetheless, there are certain health advantages to some carbs. People who want to follow a less restrictive diet plan should eat a range of fiber, nutrient-dense carbohydrates, like fruits and vegetables, as well as healthy fats and protein sources.
FAQs
The ketogenic diet: what is it?
Diet Review: The Nutrition of the Ketogenic Diet for Weight Loss: What Is It? For decades, people have utilized the low-carb, high-fat ketogenic diet, sometimes known as the “keto” diet, to treat a variety of illnesses. The ketogenic diet was widely utilized to help manage diabetes in the 19th century.
Which foods fit within the ketogenic diet?
Fish and shellfish, meat and poultry, avocados, berries, nuts and seeds, eggs, high-fat dairy products, olive oil and other oils, high-cocoa chocolate, and non-starchy vegetables like bell peppers, broccoli, and zucchini are all foods that are acceptable on the ketogenic diet.
What are the nine keto rules?
Key guidelines for the ketogenic diet are:
Don’t exceed 25g of net carbohydrates per day.
Keep 70–75% of your calories from fat.
Limit your protein intake to 20–25%.
Drink plenty of water.
Pay attention to whole foods.
Steer clear of processed foods.
Add vegetables that are high in fiber.
Pay close attention to macros.
Does keto help people with epilepsy?
Keto diet for epilepsy, or ketogenic diet. Patients with uncontrolled epilepsy can be treated with the ketogenic diet. The diet, which is low in carbohydrates and heavy in fats, alters how the brain obtains energy to function. Despite its lack of clarity, this diet has helped many people experience fewer seizures.
Does keto work or not?
The fact that keto is not a sustainable diet is a major factor in why many medical specialists advise against it, according to Beaver. “While it’s wonderful to see weight loss at the start of a ketogenic diet, research indicates that most people will regain their prior weight or possibly gain more after stopping.
Are bananas ketogenic?
Bananas. Bananas are essentially off the table when following a ketogenic diet, even though they have many health benefits, including strengthening the heart and immune system. Why? You can nearly reach your daily carbohydrate quota by eating one medium banana, which has a substantial 27 grams.
Is milk okay to consume when on keto?
For many people, milk and related dairy products are a necessary part of their diet. Cow’s milk is not appropriate for a ketogenic diet since it contains a lot of lactose, a form of carbohydrate. For many people, milk and related dairy products are a necessary part of their diet.
What are the three drawbacks of the ketogenic diet?
Low blood pressure, kidney stones, constipation, vitamin shortages, and an elevated risk of heart disease are all possible side effects of the ketogenic diet. Keto and other strict diets may also lead to disordered eating or social isolation. People with disorders affecting their thyroid, liver, gallbladder, or pancreas should not follow the ketogenic diet.
What fruits are suitable for a ketogenic diet?
By definition, keto fruits are low in carbs. To stay within the keto diet’s bounds, you still need to watch how much of the majority of keto-friendly fruits you eat. Avocados, watermelon, strawberries, lemons, tomatoes, peaches, raspberries, cantaloupe, star fruit, and blackberries are among the fruits that are good for a ketogenic diet.
Reference
- Cissn, R. M. M. (2023, November 7). The Ketogenic Diet: A detailed beginner’s guide to keto. Healthline. https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/ketogenic-diet-101#supplements
- What’s a ketogenic diet? (n.d.). WebMD. https://www.webmd.com/diet/ss/slideshow-ketogenic-diet
- Harvard Health. (2024, March 28). Should you try the keto diet? https://www.health.harvard.edu/staying-healthy/should-you-try-the-keto-diet
- Gotter, A. (2024, January 24). Is the keto diet good for you? https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/319196#takeaway
- Ld, S. S. M. R. (2023, February 23). 20 foods to eat on the keto diet. Healthline. https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/ketogenic-diet-foods