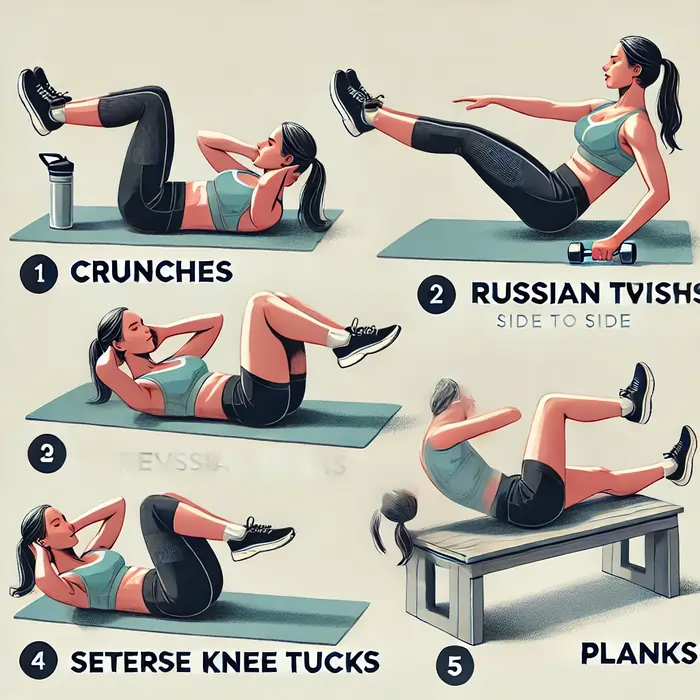
Strengthening Exercises
Introduction
Strengthening exercises are a form of physical activity aimed at improving muscle strength, endurance, and power. Weights, resistance bands, or body weights are used to provide resistance to muscle contraction.
Muscles are made to work against a weight or force during strength training, sometimes referred to as resistance exercise, in order to build muscle strength.
Plyometrics, resistance bands, weight machines, free weights, and utilizing your own body weight are some of the several types of strength training. A novice should train two or three times a week to maximize their benefit.
A pre-participation health examination and consultation with a physician, exercise physiologist, physiotherapist, or other certified exercise specialist are recommended before starting a new fitness program. The best programs will produce the greatest outcomes if they have clear objectives, beginning points, and progressions.
Principles of Strengthening Exercises
The foundations of a strength training program are as follows:
- The Overload Principle states that in order to overcome muscular accommodation and produce and maintain physiological adaptations from strength training, it is critical to gradually overload the musculoskeletal system.
- Adaptations are particular to the muscles being worked out, according to the concept of specificity.
- Periodization: In order to optimize performance, overloading should take place at the ideal level and timing.
- Individuality: Since every person will react differently to the training stimuli, programs must be customized for each individual.
- Reversibility: If the preparing boost is absent for a long time, the preparing impacts will be lost.
Equipment of Strengthening exercises
- Squats, push-ups, and chin-ups may all be performed with body weight, which is useful, particularly when working or traveling.
- convenient, particularly when traveling or working.
When stretched, resistance bands offer resistance. They are adaptable to the majority of workouts and are portable. Throughout a movement, the bands - Suspension equipment is a type of training device that performs a range of workouts using the user’s body weight and gravity. Creating a Resistance Strength Training Program. Focussing on form and safety is essential to reducing the risk of harm. When creating a protocol, the following are the main considerations:
Designing a Strength Exercise (Resistance)
Focusing on form and safety is essential to reducing the risk of harm. The primary factors to take into account when designing a protocol are:
- Choice: This idea allows people to be independent and to have some control over their training regimen, which may be customized to fit their specific needs, preferences, and abilities. Giving people a choice can evoke a response that encourages program adherence, engagement, and motivation. All things considered, this idea can offer a more effective training schedule and open the door to a fruitful strength program.
- Order: Perform 80–90% of your one-rep maximum weight for 3-5 sets of 1-2 reps, followed by a 2- to 5-minute rest period. Workout efficiency, general strength, and functional growth can all be directly impacted by the sequence in which exercises are performed. The most important lesson to be learned from this approach is to give each workout your best effort. Exercise selection, exercise priority, multi-joint versus single-joint, and fatigue consideration are other considerations to take into account in order.
- Frequency: The frequency concept describes how frequently a person works out a particular muscle group over a predetermined period of time in order to increase strength or heal a deficiency. In order to achieve quality strength development and impairment restoration, this approach focuses on establishing a well-balanced relationship between training frequency and recovery.
- An intensity: metric that can be used to customize a workout program for each person is the rate of perceived exertion scale (RPE). The modified RPE scale, which has a range of 1 to 10, with 1 denoting extremely easy and 10 denoting maximal exertion, is available for use by individuals.
- Volume, Rest, And Type of Muscle Strengthening:
- Rest, Volume, and Type of Muscle Strengthening Volume can be determined by the number of sets, repetitions, or workouts a person performs each week. More than twice a week is the ideal frequency for strength training. These are recommendations for exercises that involve a lot of joints, such as benches, and squats.
- Strength: requirements are: 2–6 sets, fewer than 6 reps per set, weight above 85% of the 1 rep maximum, and 2–5 minute rest intervals in between sets.
- Power: Complete three to five sets of one to two repetitions with 80 to 90 percent of your one-rep maximum weight, and then take two to five minutes to recover.
- Hypertrophy:
- 30-90 seconds of rest, 6-12 repetitions, 3-6 sets, and 67-85% of the maximum weight for one rep.Muscles’ Persistence.
- 2–3 sets, over 12 repetitions, fewer than 30 seconds of rest, and less than 67% of one rep maximum are all indicators of muscular endurance.
- Strength training progression: Careful thought and precise planning are necessary when creating a strength (resistance) training program. The most effective strength training regimen is one that is customized for each individual. The four categories of resistance programs are listed below. should be customized based on each person’s one-rep maximum and Rate of Perceived effort (RPE) scale to determine their level of effort. People should gradually increase the weight they utilize for their exercises as they get stronger. Changing the exercises’ pace is another component of growth. Slowing down an exercise may make it more difficult. When progressing workouts, other elements including torque, time under tension, and range of motion are taken into account.
- It takes significant thought and precise preparation to create a strength (resistance) training program. The most effective strength training regimen is one that is customized for each individual. The four categories of resistance programs are listed below.
Strength
It takes significant thought and precise preparation to create a strength (resistance) training program. The most effective strength training regimen is one that is customized for each individual. The four categories of resistance programs are listed below.
Goal: Increase muscle strength with an emphasis on both eccentric and concentric contractions. Boost your total muscular strength and enhance your performance during force-producing exercises. Prioritise training plans that combine the greatest amount of strength and speed.
Design considerations: Include compound movements like squats, deadlifts, bench presses, and rows that focus on the main muscle areas. Boost your total muscle mass and enhance your performance during force-producing exercises. Give top priority to training regimens that combine the most strength and quickness. There will be a reduction in the chance of injury and an improvement in balance and coordination. Consequently, making daily living activities simpler.
Power
It takes significant thought and precise preparation to create a strength (resistance) training program. The most effective strength training regimen is one that is customized for each individual. The four categories of resistance programs are listed below.
Goal: Increase speed and explosiveness to improve the capacity to produce maximum force in the shortest amount of time, which is essential for sports involving rapid motions like throwing, jumping, and running.
According to the plan’s principle, single exertion lifts should be 80–90% of 1RM reps, while multiple exertion lifts should be 75–85% of 1RM with 3-5 reps. Both should have three to five sets with two to five minutes of rest in between. Power training requires exercises that are relatively rapid, have a load, and have an explosive goal.
Hypertrophy
It takes significant thought and precise preparation to create a strength (resistance) training program. The most effective strength training regimen is one that is customized for each individual. The four categories of resistance programs are listed below.
Goal: Encourage muscular growth and hypertrophy by doing resistance training in a certain manner. concentrating on appearing “aesthetic.”
Include direct-to-high volume training with direct loads 67-85% of 1RM in sets of 3-6, performing 6-12 repetitions while taking 30-90 seconds off in between sets, in accordance with the plan’s considerations. Focus To target particular muscular parts like the shoulder, triceps, and biceps, isolation exercises should be incorporated. To maximize the development of hypertrophy, progressive overload—such as increasing weight, repetitions, sets, or even decreasing rest time—is always recommended.
It takes significant thought and precise preparation to create a strength (resistance) training program. The most effective strength training regimen is one that is customized for each individual. The four categories of resistance programs are listed below.
expanded portability and useful capacity, progressed quality of life variables, decreased body fat, expanded metabolic rate, decreased blood weight and cardiovascular strain amid physical activity, a better lipid profile, and a decreased risk of type II.
Muscular Endurance
It takes significant thought and precise preparation to create a strength (resistance) training program. The most effective strength training regimen is one that is customized for each individual. The four categories of resistance programs are listed below.
Objective: Boost muscle endurance and stamina by lengthening workouts and boosting resistance to exhaustion. Boost your aerobic capacity and cardiovascular fitness, which are crucial for tasks requiring sustained effort.
Effects of Strengthening Exercises
It takes significant thought and precise preparation to create a strength (resistance) training program. The most effective strength training regimen is one that is customized for each individual. The four categories of resistance programs are listed below.
Numerous beneficial neuromuscular changes that improve mental and physical health are triggered by strength training. Resistance training offers numerous benefits for mental and physical well-being, such as:
- increased tone and strength of the muscles.
- preserving one’s balance, mobility, and flexibility as one ages can help one stay independent.
- Controlling weight and increasing the muscle-to-fat ratio may be even more beneficial for fat loss than aerobic exercise.
- may lessen or stop older people’s cognitive decline.
- Increased stamina: You won’t tire as quickly as you gain strength.
- prevention or management of long-term conditions like obesity, diabetes, heart disease, arthritis, back pain, and depression.
- Pain control
- The strength (resistance) training program design calls for significant thought and meticulous preparation. The finest strength training regimen is one that is customized to meet individual objectives. These are the four categories of resistance programs.
- better posture.
- reduced chance of harm.
- greater thickness and quality of bones and a diminished hazard of osteoporosis.
- Enhanced well-being: Resistance exercise may increase mood, body image, and self-confidence.
- better sleep and prevention of insomnia.
- increased use of blood glucose.
- decreased blood pressure at rest.
- improved lipid profiles in the blood.
- accelerated transit time in the gastrointestinal tract
Strength Exercises and Chronic Diseases
It takes significant thought and precise preparation to create a strength (resistance) training program. The finest strength training regimen is one that is customized to meet individual objectives. The four categories of resistance programs are listed below. Chronic conditions such as diabetes, asthma, metabolic syndrome, cardiovascular disease, low back pain, arthritis, joint pain, depression, and COPD can all be improved by exercise.
Strength exercise can increase muscle endurance and strength, facilitate daily tasks, decrease the loss of muscle strength caused by disease, and stabilize joints.
Obesity
It takes significant thought and precise preparation to create a strength (resistance) training program. The most effective strength training regimen is one that is customized for each individual. The four categories of resistance programs are listed below. Strength exercise can increase muscle endurance and strength, facilitate daily tasks, decrease the loss of muscle strength caused by disease, and stabilize joints.
Fat accumulation, metabolic slowing, and muscle loss are the results of sedentary lifestyles.
Nearly 70% of adult Americans are overweight today, putting them at higher risk for chronic illnesses and other health issues. In the US, less than 5% of persons regularly perform endurance exercises.
Strength training offers a useful strategy for overcoming obesity and producing mental and physical changes that enhance quality of life. Simple, short strength training sessions have been shown to be beneficial for improving a number of health and fitness aspects, including fat reduction, metabolism recharge, and muscle growth.
Cardiovascular Disease (CVD)
It takes significant thought and precise preparation to create a strength (resistance) training program. The most effective strength training regimen is one that is customized for each individual. The four categories of resistance programs are listed below.
An 18% decrease in significant cardiovascular events is linked to the size of resistance exercise-induced drops in SBP (5–6 mmHg) and DBP (3–4 mmHg) (Blood Pressure Lowering Treatment Trialists Collaboration, 2014). According to Mcleod et al. (2019), even people with CVD or at risk of acquiring it can benefit from low-to-moderate intensity resistance exercise training (RET) (30–69% of 1RM).
It takes significant thought and precise preparation to create a strength (resistance) training program. The most effective strength training regimen is one that is customized for each individual. The four categories of resistance programs are listed below.
It is advised to follow a thorough resistance-training regimen consisting of 8–10 exercises for 20–30 minutes at an intensity of ˜50±10% of 1 RM at least twice a week, Exercise should be performed without the Valsalva maneuver and at a level that is comfortable for you (13 to 15 on the RPE [rating of perceived exertion]).
If the individual can lift the weight for 12 to 15 repetitions without experiencing discomfort, then raising the weight by 5% is a good way to progress the exercise. The weight should be decreased if the athlete is unable to perform the required minimum number of repetitions (8 or 10) with proper form.
Type 2 Diabetes
It takes significant thought and precise preparation to create a strength (resistance) training program. The most effective strength training regimen is one that is customized for each individual. The four categories of resistance programs are listed below.
According to a 2014 American Diabetes Association study, medicine with a stronger focus on aerobic exercise training was not as effective at lowering glycaemic control as lifestyle changes, such as diet and exercise. Other research, however, indicates that resistance training improves glycemic control.
The degree of resistance exercise intensity in glycaemic control is contradicted by the results. However, the 2019 study by Mcleod et al. Recommends include weight training for the entire body twice a week, regardless of the level of difficulty.
Cancer
It takes significant thought and precise preparation to create a strength (resistance) training program. The most effective strength training regimen is one that is customized for each individual. The four categories of resistance programs are listed below. Resistance training has been shown to improve prognosis during adjuvant therapy and lower cancer risk, recurrence, and mortality.
Resistance exercise has been shown to be effective in prostate and breast cancer. The best dosage, level of intensity, and mechanisms underlying the cancer-preventive effects of resistance exercise require more research.
Strength and the Older Population
It takes significant thought and precise preparation to create a strength (resistance) training program. The most effective strength training regimen is one that is customized for each individual. The four categories of resistance programs are listed below. Age-related weakness and a variety of co-morbidities are inevitable.
The three most prevalent diseases that reduce physical mobility and raise the risk of falls are frailty, sarcopenia, and osteoporosis. Enhancing functional mobility can be greatly aided by resistance training. Resistance training is a powerful way to increase bone density and muscle mass, which is impacted by osteoporosis and sarcopenia.
It takes significant thought and precise preparation to create a strength (resistance) training program. The most effective strength training regimen is one that is customized for each individual. The four categories of resistance programs are listed below. The most effective strength training regimen is one that is customized for each individual. The four categories of resistance programs are listed below.
The most effective method for increasing functional mobility in older persons has been shown to be resistance training mixed with aerobic and balance activities. According to recent research, older adults may not be getting enough protein from the prescribed levels, thus increasing protein consumption and strength training can be quite helpful. View Protein and Muscle Function.
Repetition Maximum for Weight Training
The largest weight an individual can lift for a predetermined number of exercise movements is known as their repetition maximum (RM). For example, a person could lift 10RM of weight for 10 consecutive repetitions of an activity. A person’s current strength level can be accurately gauged by their RM.
The most weight a person can lift for a single repetition with proper form is known as their One Repetition most (1RM).
Strength and conditioning coaches most frequently utilize the 1RM test to evaluate training program efficacy, strength imbalances, and strength capacities.
You may see a person’s progress by setting up and monitoring 1RM. Because it is a precise metric, it can be used to assess the program’s effectiveness.
Your 1RM can be estimated using a variety of formulas, each with somewhat different computations. The most popular one is Matt Brzycki’s Brzycki formula, which has been shown to be accurate.