HDL Cholesterol
HDL Cholesterol (High-Density Lipoprotein): Often referred to as “good” cholesterol, HDL helps transport excess cholesterol from the bloodstream and artery walls to the liver for excretion or reuse. A lower risk of heart disease and stroke is linked to higher HDL levels.
It plays a protective role by reducing plaque buildup in arteries, promoting cardiovascular health. Lifestyle factors such as regular exercise, a healthy diet rich in unsaturated fats, and avoiding smoking can help maintain optimal HDL levels.
What is HDL?
High-density lipoprotein is referred to as HDL. Your blood contains this particular form of lipoprotein.
Lipids (fats) and proteins combine to form lipoproteins. Their primary function is to move lipids, such as cholesterol, to the cells in your body that require them. Because of their chemical makeup, fats cannot move through your blood independently; they need a ride. To reach where they need to go, lipoproteins must assist them.
HDL cholesterol: what is it?
HDL cholesterol is the same as HDL. When discussing these particles and their function in heart health, most people use both terms.
Despite containing proteins and lipids, HDL particles are recognized by the type of fat they carry, cholesterol.
Why is HDL referred to as “good cholesterol”?
Because HDL aids in the removal of excess cholesterol from the body, it is referred to as the “good cholesterol.” Your risk of cardiovascular disease may be reduced by this technique.
Normally, cholesterol leaves your liver and enters your circulation. Lipoproteins then transport the cholesterol to various bodily cells to support vital processes (such as assisting your body in producing hormones and forming cell membranes).
Sometimes, however, your blood contains too much cholesterol. Your body doesn’t need that much. In this case, reverse cholesterol transfer is beneficial. Because reverse cholesterol transfer is a complicated bodily process, scientists are still trying to figure out how and when HDL is involved. HDL particles are known to be able to return excess cholesterol to the liver from circulation. Afterward, this cholesterol is broken down by your liver and eliminated from your body through feces.
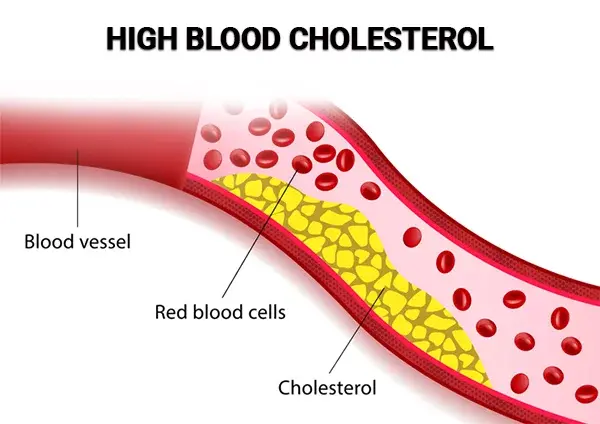
This is advantageous since high blood cholesterol increases the risk of atherosclerosis or plaque accumulation in the arterial walls. HDL is the beneficial cholesterol that is produced by eliminating excess cholesterol.
However, it does more than that. To maintain the strength of your cells, HDL cholesterol also fights oxidants and inflammation. Additionally, it contributes to the prevention of blood clots.
How can I determine my level of HDL cholesterol?
A lipid panel blood test might be ordered for you by your healthcare physician. You’ll be given numbers for your HDL and other types of cholesterol.
What is a suitable HDL level?
An HDL of 60 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) or more is ideal. This can reduce your risk of cardiovascular (heart and blood vessel) disorders, such as heart disease and stroke, according to research.
What is an HDL level that is unhealthy?
When HDL cholesterol levels are outside of the usual range, it is considered harmful. A harmful level of HDL is present in those with low levels. However, an excessively high amount can also encourage the advancement of atherosclerosis. Various medical conditions might induce very high or low HDL values.
What is meant by low HDL cholesterol?
Your HDL cholesterol may be low for a variety of causes, such as:
Tangier illness: Your HDL cholesterol is abnormally low due to this genetic disease.
combined hyperlipidemia in the family: Your HDL cholesterol is too low and your LDL cholesterol is too high due to this inherited disease.
lack of ApoA1: Apolipoprotein A1 is insufficient in those who have this genetic disorder. This is an essential part of HDL.
Metabolic syndrome: Lower-than-normal HDL levels are one of the risk factors for cardiovascular disease.
A body mass index (BMI) of above 25 (obesity/overweight). Your HDL level may drop if you are overweight.
tobacco use or smoking: Nicotine, which is found in tobacco, reduces HDL levels. This negative effect is present in all tobacco products, including e-cigarettes.
insulin resistance: Your body’s insulin may have a harder time controlling your blood sugar if you have too much fat. A low HDL level may result from this.
medications you take: Your HDL cholesterol level can be lowered by some medications, such as beta-blockers, hormones, or diuretics.
What does it signify if my HDL is elevated?
Anything over 80 mg/dL is considered elevated, or unusually high, HDL levels.
A genetic mutation can be one factor contributing to elevated HDL cholesterol. Gene mutations may result in excessive HDL cholesterol production or difficulties eliminating it from the body. For instance, a mutation in the CETP gene may result in HDL levels exceeding 150 mg/dL.
Additional reasons for unusually elevated HDL may include:
- hyperthyroid condition.
- gallbladder cholangitis.
- alcohol addiction.
- certain drugs.
- After looking into the source of your elevated HDL, your healthcare professional will determine whether you require therapy.
The best way to increase your HDL
The best way to increase your HDL is to consult your healthcare practitioner for recommendations relevant to your requirements and any medical concerns you may have. In general, a few lifestyle modifications can help boost your HDL level, including:
Consuming heart-healthy meals: According to research, the Mediterranean diet can help lower cholesterol and enhance heart health in general. This diet consists of whole grains, legumes (beans and lentils), and an abundance of fruits and vegetables. Additionally, eating foods high in omega-3 fatty acids can increase your HDL cholesterol.
Avoiding or consuming fewer unhealthy meals: Avoid clear baked products or fried doughnuts that contain trans fats (partially hydrogenated oils). Eat less saturated fat, such as that found in butter, cheese, bacon, and sausage.
Do some exercise: Your HDL cholesterol can rise with aerobic exercise. Five days a week or more, try to get in at least 30 minutes of exercise. It’s acceptable to not have exercised much in the past. Work your way up from only five or ten minutes a day. However, before beginning any new fitness regimen, make sure to see your provider.
Keeping your weight within a healthy range: Enhancing HDL levels is facilitated by weight loss, particularly around the stomach.
Avoiding all forms of tobacco use: HDL is lowered by smoking, vaping, and other tobacco use. Thus, avoid starting to use tobacco if you don’t already. And if you do, you should focus on quitting. Consult your healthcare provider about quitting techniques. Secondhand smoke is dangerous as well. For both your benefit and theirs, if you live with someone who smokes, offer to help them stop.
Taking medication: Your doctor can recommend drugs like ezetimibe or PCSK9 inhibitors to help raise your HDL.
FAQs
What happens if your HDL is low?
Combining low HDL and/or high LDL cholesterol with high triglyceride levels can raise your risk of heart attack and other health issues. Find out more about ideal levels of triglycerides and cholesterol in the blood.
How do I raise HDL?
Physical Activity: Walking, riding, weight training, and using the stairs are all important.
Giving up smoking will raise HDL and lower the risk of heart disease and several types of cancer.
Weight Loss: If you are overweight, losing 5–10% of your body weight might raise your HDL cholesterol.
What fruit is good for cholesterol?
Whether you choose dragon fruit, kiwi, oranges, berries, or apples, fruits provide a sweet and tasty treat that is rich in fiber and antioxidants that can help decrease cholesterol and strengthen the heart. Fruit should be a part of your daily diet, whether it is as a snack or as a smoothie.
What are the 5 signs of high cholesterol?
heart attack. A cholesterol issue will lead to cardiac difficulties, as you are well aware.
high blood pressure. You should also be on the lookout for high blood pressure.
Diabetes, angina, chest discomfort, etc.
Pain when walking. Stroke.
What is the best morning drink for cholesterol?
Red wine, soy milk, pomegranate juice, citrus juice, green tea, and plant-based smoothies are some of the finest beverages for controlling cholesterol.
References:
- Professional, C. C. M. (2025, January 6). HDL cholesterol. Cleveland Clinic. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/articles/24395-hdl-cholesterol




21 Comments