Abdominal (Android) Obesity
Introduction
Abdominal (Android) Obesity refers to excessive fat accumulation in the abdominal region, primarily around the visceral organs. This fat distribution pattern is more common in men and is associated with a higher risk of metabolic disorders, including type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and insulin resistance.
It is often linked to factors such as genetics, poor diet, sedentary lifestyle, and hormonal imbalances. Measurement methods include waist circumference and waist-to-hip ratio, with management focusing on dietary changes, physical activity, and lifestyle modifications.
Many people are unaware that there are several types of obesity, despite the fact that 42% of American adults are obese. A particular kind of obesity that presents several health hazards is called android.
The accumulation of excess body weight on the torso is known as android obesity. Android obesity, sometimes known as male-pattern obesity, apple-shaped obesity, or abdominal obesity, is more prevalent in men.
Android obesity is mostly caused by lifestyle choices such unhealthful eating and inactivity, although heredity has also been implicated. A higher chance of acquiring android obesity may exist for those with a family history of the disorder. Type 2 diabetes, hypertension, and heart disease are just a few of the major health issues that can result from Android obesity.
If you suffer with android obesity, it’s critical to collaborate with a healthcare professional in order to reduce weight. Fortunately, those who suffer from the illness typically have an easier time losing weight than those who suffer from other forms of obesity, and even a small reduction in weight can have several health advantages.
When an obese person has Android Obesity, their excess body fat is dispersed throughout their abdomen, giving the appearance of an apple cut. In this instance, the human body’s fat is primarily distributed throughout the shoulders, chest, and even the neck. It is observed that males experience this more frequently than females. Cardiovascular and cardiac issues are also consequences of obesity in androids.
A number of genetic and environmental variables contribute to obesity in Android. It is heavily influenced by genetic factors. Android obesity is more likely to occur in subsequent generations if there is a family history of it. A person is deemed obese if their body weight is 20% more than it should be. An individual is diagnosed with Android Obesity Disease if their body mass index is 30 or more.
HOW DO WE DISCUSS OBESITY?
We must first define “obesity” in order to comprehend Android obesity. The body mass index, or BMI, is typically used to detect overweight or underweight. To calculate this, divide the weight in kilograms by the square of the height in meters, or weight (kg)/height. The subsequent figure can then be used to assess the individual’s level of obesity. The BMI can be used to differentiate between the following types of obesity:
- Moderate obesity: This happens when a person’s BMI falls between 30 and 35.
- Severe obesity: When a person’s BMI falls between 35 and 40, they are considered obese.
- Morbid obesity: When the BMI is more than 40, it happens.
ANDROID OBESITY: WHAT IS IT?
However, determining BMI alone is insufficient to define obesity. In fact, we cannot identify the location of excess body fat only on our knowledge of this index. Because of this, researchers have differentiated between gynoid and android obesity.
The term “Android obesity” describes a type of obesity where the extra fat mass is distributed in the upper torso. Those who suffer from this type of obesity are especially prone to have excess fat on their faces and abdomen. Android obesity is sometimes referred to as abdominal obesity. In guys, this type of obesity is extremely prevalent. The male sex hormone, testosterone, is, in fact, intimately related to it. However, because postmenopausal women’s estrogen levels are gradually declining in favor of testosterone, android obesity can also develop in these women.
Android Fat Distribution
The term “central” fat storage, sometimes referred to as “android fat storage,” describes the main distribution of body fat in the central thoracic area, which encompasses the belly and trunk. Because of this distribution, those with excess android fat will seem “apple-shaped,” with the waist significantly greater than the hips.
Android fat is kept more “viscerally,” that is, in and around the organs in the peritoneal cavity (abdominal cavity), as opposed to subcutaneously, as gynoid fat is. This has the effect of compressing and limiting blood flow to the essential organs, which can result in problems like insulin resistance because of the changes in hormone profiles.
Obesity-related disorders can result from excess fat in this location.
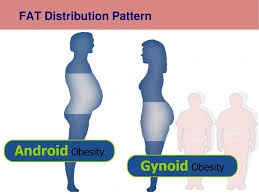
Android vs. gynoid obesity
Due to its association with an increased risk of heart disease, high blood pressure, sleep apnea, diabetes, some types of cancer, and stroke, Android obesity may be more dangerous than gynoid obesity. On the plus side, it’s usually easier to reduce excess weight linked to android obesity than gynoid obesity.
It’s simple to identify the type of obesity you have since the location of the excess weight distinguishes gynoid obesity from android obesity. You must first calculate your body mass index. A body mass index (BMI) calculator, like the one offered by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), can be used for this.
You can then measure your waist circumference to find out where you carry the excess weight if you are fat. Note the number on a tape measure that is placed directly over the hip bones. Android obesity may be indicated by a circumference of more than 35 inches for women and 40 inches for men.
If your BMI is over 30, but your waist circumference is less than these, you can have gynoid obesity. Importantly, waist circumference and BMI do not apply during pregnancy. If you are pregnant, you should talk to your obstetrician (OBGYN) about any weight issues you may have.
Researchers and medical professionals now understand that bad health practices are not the only factor contributing to android obesity. Numerous elements contribute to the complexity of the problem. These may include hormonal, nutritional, environmental, behavioral, or hereditary factors. It’s crucial to talk about each of these aspects with your healthcare physician in order to decide what actions to take to reach a healthy weight.
WHICH ARE THE PRIMARY CAUSES?
Above all, you need to keep in mind that age, but particularly gender, contributes to the distribution of body fat. Conversely, there are a number of reasons why Android obesity may occur.
- Heredity: It should be mentioned that having an obese parent increases your chances of getting android obesity by 25%. If it is present in both parents, the risk rises to 80%.
- Sedentariness: It is more common for fat to be stored in the upper body when there is a lack of physical activity and constant sitting.
- Excessive food consumption: One of the main causes of Android obesity is also eating past fullness and grabbing for high-fat foods.
- Using drugs that contain corticosteroids
- A poor way of life
- neurological and genetic issues
- Hormonal disorders: This cause holds great significance for women.
- Slower metabolism: This makes it harder for the body to adequately burn fat.
- Increased blood insulin levels
RISKS CONNECTED WITH THIS TYPE OF OBESITY
Android obesity is the most hazardous of the various types of obesity. Intra-abdominal fat can encircle a number of essential organs, making it impossible for them to function, which explains why it is harmful.
Android obesity can have a number of negative effects and hazards, such as:
- When type 2 diabetes first appears
- Myocardial infarction, stroke, excessive blood pressure, and other cardiovascular conditions are among them.
- Steatosis and hepatitis are two examples of liver illnesses that can occur.
- The prevalence of some respiratory disorders, such as sleep apnea
Other problems could potentially happen in addition to this. It’s true that widespread exhaustion, dyspnea, and a variety of joint issues are common in obese Androids.
How can abdominal obesity be combated?
You can develop specific behaviors to prevent the negative effects of this type of obesity and to protect your health. There are rather drastic options, like surgery, if the obesity is extremely severe.
In any case, here’s how to combat belly obesity.
- Change your diet: You must concentrate on eating meals high in fiber, such fruits and vegetables, to do this. Proteins like fish or lean meats should make up the remaining 25% of your diet, with these making up the remaining 75%.
- Be physically active: Exercise on a regular basis can help reduce belly fat. Ideally, cardiovascular exercises like swimming, walking, or running are recommended.
- Opt for interval training: This include engaging in vigorous physical activity for a brief while before reducing the intensity.
A nutrition specialist should always be consulted, regardless of the remedy you decide on.
Conclusion
Results would be better and faster if these forms of obesity were addressed early on. Because the causes and effects are distinct, you can work with a team of experts to create a plan of action that properly meets your needs.
Make sure you are making an effort to eliminate these body fats in order to prevent any long-term hazards or health issues that could harm you later on. Maintain your health by leading a healthy lifestyle. Additionally, be aware of typical blood sugar levels.
FAQs
How is gynoid obesity different from android obesity?
Obesity can be broadly categorized as either gynoid or android depending on where the bodily fat accumulation occurs.Gynoid fat builds up around the thighs and hips, whereas android fat concentrates around the abdomen.
What is the obesity pattern of androids?
Known as “central” fat stores, Android fat stores are primarily found in the upper body or in the trunk/abdominal region. People with extensive android fat patterns will appear “apple-shaped,” with a waist significantly greater than the hips, as a result of this distribution.
How can I get rid of obesity in androids?
With a healthy diet and regular exercise, Android fat can be managed. An unhealthy diet combined with inactivity is likely to raise an Android’s body fat percentage.
What symptoms indicate Android obesity?
Indices of Obesity in Android
Common signs include love handles, a bulging belly, and a waist diameter that is greater than the hip circumference. Along with back pain and a higher chance of developing conditions like diabetes and heart disease, patients may also have trouble getting into garments.
What factors contribute to Android obesity?
Although the development of this condition is influenced by environmental variables, hereditary factors play a major role in its incidence in families. The metabolic abnormalities that also define syndrome X—dyslipidemia, arterial hypertension, and insulin resistance—are linked to Android obesity.
The body of the android is where?
This fat builds up around the middle part of the trunk. It may also encompass the upper arms and chest. Increased insulin resistance may result from storing fat mostly in the arms and chest.
What is the ratio of Android to Gynoid?
The term “gynoid” (pear-shaped) describes the storage of fat around the hips. More Android is represented by a larger number, and more Gynoid by a smaller number. Ideal values are thought to be less than 0.8 for women and 1.0 for men from the perspective of health risk.
How is Android obesity diagnosed?
Just above the hip bones, place a tape measure, then record the number.An android may be obese if their circumference is greater than 35 inches for women and 40 inches for men.
How can I lose fat on my Android phone?
Regular moderate-intensity aerobic exercise, such as jogging, cycling, hiking, swimming, etc., for 30 to 60 minutes will effectively lower visceral fat reserves and raise HDL levels.
What proportion of Android is considered normal?
Your android fat should always be less than your gynoid fat, and your A/G ratio should be less than 1.0. Tissue Fat % for Android: 53.3%Gynoid Tissue %Fat: 40.6% Tissue %Fat: 1.31 A/G ratio.
How can I get rid of my belly in seven days?
Check out these suggestions for burning abdominal fat in less than a week as well.
Make aerobic activities a part of your everyday schedule.
Limit processed carbohydrates.
Increase your intake of fatty fish….
Eat a breakfast rich in protein to start the day.
Make sure you get adequate water.
Limit your consumption of salt.
Take in soluble fiber.
Reference
- What is android obesity? (n.d.). https://blog.walgreens.com/health/general-health/what-is-android-obesity.html#:~:text=Android%20obesity%20occurs%20when%20excess,obesity%20or%20male%2Dpattern%20obesity.
- Just a moment. . . (n.d.). https://hiro.care/how-does-android-obesity-present-itself-and-how-to-treat-it
- Android Obesity | List of High Impact Articles | PPTs | Journals | Videos. (n.d.). https://www.omicsonline.org/scholarly/android-obesity-journals-articles-ppts-list.php
- What does Android and Gynoid mean in Phoenix Advanced for body fat? (n.d.). https://www.styku.com/help/search/what-are-the-android-and-gynoid-regions-of-the-body