Brown Fat (Brown Adipose Tissue)
Brown fat, also known as brown adipose tissue (BAT), is a type of body fat that helps generate heat by burning calories. Unlike white fat, it plays a key role in regulating body temperature and supporting metabolism, making it beneficial for energy balance and weight management.
What is Brown Fat?
- One type of body fat that helps keep you warm in cold weather is brown fat, also known as brown adipose tissue. Additionally, brown fat aids in calorie burning and reserves energy. In chilly weather, brown fat begins to function, or activate.
- When you get too chilly, brown fat, also known as brown adipose tissue, helps keep your body temperature stable. Bears use this similar fat to stay warm during their hibernation.
- There is a lot of dark fat behind the shoulder blades of newborns. One of the ways the body produces heat is through shivering, which is not possible for newborns. Brown fat serves as an internal warmer. As you age, you lose most of it and develop a shivering reaction to cold temperatures.
What kinds of fat are there in my body?
You have several kinds of fat in your body. Healthcare professionals use color and function to distinguish between different types of fat, such as:
White fats:
- Your body is mostly composed of white fat. Energy is stored by white fat in different parts of your body. White fat protects your inside organs. Obesity results from excess white fat.
- You are probably familiar with white adipose tissue (WAT), which is the typical type of fat. Your body stores your energy in big fat droplets that build up all over the place. Your organs are literally insulated by the fat buildup, which keeps you warm.
- Obesity can be caused by excess white fat in people. Additionally, an excess of white fat around the waist may increase the risk of diabetes, heart disease, and other conditions.
Brown fats:
- Compared to white fat, brown fat is smaller. It controls your body temperature by storing energy and burning it. By generating heat just before your body begins to shiver, brown fat aids in calorie burning (thermogenesis). It also aids in the regulation of fat and sugar (glucose) metabolism.
- White fat has a larger energy storage capacity than BAT. It obtains its color from the large number of mitochondria that are rich in iron. Heat is produced by burning brown fat without causing shivering. This is referred to as thermogenesis. Brown fat burns calories in the process as well.
- Some metabolic disorders and obesity may be treated with brown fat.
- Brown fat was once thought to be unique to infants, according to scientists. Additionally, they believed that this fat vanished by the time the majority of people reached maturity.
- Researchers now know that brown fat reserves are minimal even in adults. Usually, the neck and shoulders are where it is kept in tiny concentrations.
- Everybody has a certain amount of “constitutive” brown fat, which is the type you are born with. There is an additional “recruitable” form. This indicates that in some situations, it can transform into brown fat. White fat and muscles all over your body contain this recruitable type.
Beige fat
White and brown fat cells combine to form beige fat. By turning white fat cells into brown ones, these cells burn calories to control body temperature.
What is the function of brown fat?
Your body uses brown fat to generate heat, which warms your blood. Because brown fat activates (turns on) in cold temperatures, you will see it burning just before you begin to shiver. It breaks down fat molecules and blood sugar (glucose) to produce heat. In order to keep your body temperature stable, this process (thermogenesis) produces heat.
How can my body benefit from brown fat?
Your body benefits from brown fat in several ways, including:
- keeps your body temperature stable.
- generates and retains energy.
- burns calories.
- aids in regulating insulin and blood sugar levels.
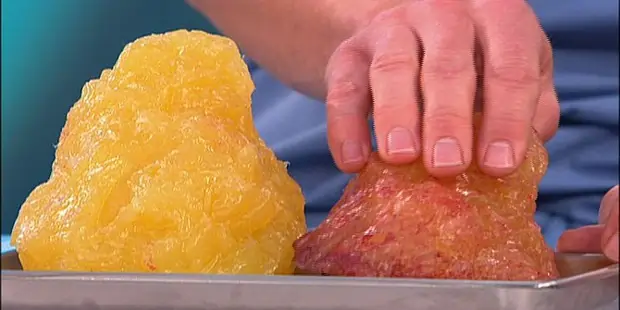
What is the appearance of brown fat?
- Brown fat is composed of tiny molecules, which are fat cells. Fatty acids and glycerol make up molecules. Because adipocytes, the cells that store brown fat in tissues, are smaller than other types of fat in your body, the structure of brown fat is more like that of muscle.
- Fat molecules bind together to form a mass when fat builds up inside your body. Brown fat appears as a tiny, lumpy, brown oval.
For what reason is brown fat brown?
Your body’s fat can be identified by its various colors. Due to a large number of mitochondria in the fat cells, brown fat is brown. The high iron content of mitochondria is what gives brown fat its color.
Where is brown fat found?
Newborns have brown fat in their shoulders, neck, and back. Brown fat disperses throughout the body between childhood and adolescence. Adults have brown fat around the neck, kidneys, adrenal glands, heart (aorta), and chest (mediastinum).
What is the amount of brown fat in my body?
- Each person has a different quantity of fat in their body. Your body contains more white fat than brown fat.
- Brown fat accounts for 2% to 5% of a newborn’s body weight. Brown fat decreases between adolescence and adulthood. You have a tiny bit of brown fat as an adult. Athletes and other slender individuals have higher levels of brown fat in their bodies.
Health Conditions and Disorders
What are some frequent conditions that impact brown fat?
Your body’s brown fat is affected by some situations, such as:
- Anorexia nervosa: A person with this eating disorder loses both white and dark fat. Your body’s energy Production is impacted by the condition, and you may experience difficulties controlling your body temperature.
- Congenital leptin deficiency: The hormone leptin is released by fat cells in adipose tissue to regulate body weight. If you have a leptin shortage, your body’s fat cells aren’t making enough of the hormone, which puts you at risk for obesity.
- Lipodystrophy: The quantity and distribution of fat tissue, or adipose tissue, in your body are impacted by this disorder. Your body has trouble storing the energy you get from eating if you have lipodystrophy.
- Lipoma: Lumps of fatty tissue beneath your skin are called lipomas. Healthcare professionals can remove the fatty tissue if it concerns you, although this condition doesn’t cause discomfort or health issues.
Which tests are frequently used to assess the condition of my brown fat?
Your doctor will do a few tests to assess the condition of your body’s fat cells, such as:
- Tests involving blood, such as a complete blood count (CBC).
- CT and PET scans.
- MRI.
Care
How can I gain body fat?
Your diet is the source of your fat. Fat is necessary because it generates energy. Good sources of fat can be found in many different foods, such as:
- Avocados.
- Nuts and seeds (flax, chia, and cashews).
- Fish (fresh tuna, salmon).
- Yogurt.
- To eat a well-balanced diet, always combine foods high in healthy fat with veggies, complete grains, dairy, and protein.
To stop harmful fat from building up in your body, stay away from the following foods:
Saturated fats (white chocolate, margarine, processed foods, and sweets).
trans fats (frozen and fried foods).
How can I make my body produce more brown fat cells?
If people wish to burn calories and lose weight, they may want to increase the amount of brown fat in their bodies. You can increase the quantity of brown fat in your body by:
- Reducing the temperature: At lower temperatures, brown fat becomes active just before you start to shiver. According to some research, lowering the temperature, having an ice bath, or taking a cold shower may stimulate brown fat, which may increase your body’s ability to burn calories.
- Including iron in your diet: The meals you eat cause you to get fat. Because brown fat is high in iron, make sure your body gets enough iron to maintain the health of your fat cells by choosing iron supplements or foods high in iron, such as meat and fish, whole grains, green vegetables, and beans.
- Consuming a balanced diet: Your health depends on your diet, particularly if you wish to gain more brown fat. According to research, certain foods, such as apples and dried fruit, contain ursolic acid, a molecule that stimulates the creation of brown fat. Avoid overindulging or consuming processed foods; instead, eat enough to satisfy your hunger.
- Exercise: One of the best ways to keep your health is to stay active. According to studies, exercise triggers the blood hormone irisin, which instructs the body to burn white fat similarly to brown fat. This procedure results in “beige fat.”
Is it possible to prevent or treat diseases like diabetes with brown fat?
Brown fat burns calories and may help regulate blood sugar and enhance insulin levels, reducing the risk of type 2 diabetes, according to a 2015 assessment of multiple studies. Additionally, it might lessen the risk of hyperlipidemia by assisting in the removal of fats from the circulation. Brown fat may be useful in treating obesity, according to other research.
FAQs
What is brown fat, and what makes it healthy?
Brown fat: Compared to white fat, brown fat is smaller. In order to control your body temperature, it saves and consumes energy. By producing heat just before your body begins to shiver, brown fat aids in the burning of calories (thermogenesis). Additionally, it aids in controlling the metabolism of fat and sugar (glucose).
What is brown fat in babies?
Because infants cannot shiver to produce heat like adults can, brown fat—a unique kind of fat in babies—generates heat to keep them warm through a process known as thermogenesis. It helps babies maintain a high core body temperature in a chilly environment and is found in places including the neck, kidneys, and chest.
What drinks activate brown fat?
Brown adipose tissue is activated by tea catechin and caffeine, which also boosts human cold-induced thermogenic capability.
Is brown fat linked to weight loss?
The body produces heat from brown fat to keep warm in cold weather, and exposure to cold can increase brown fat reserves. By increasing calorie expenditure, activating brown fat may help with weight loss efforts, according to research.
References:
- Professional, C. C. M. (2025, September 10). Brown fat. Cleveland Clinic. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/body/24015-brown-fat
- Marcin, A. (2023, May 22). Brown Fat: What you should know. Healthline. https://www.healthline.com/health/brown-fat#takeaway
- Wikipedia contributors. (2025b, November 10). Brown adipose tissue. Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Brown_adipose_tissue