Obesity Rate in US (United States of America)
Overview
In the United States, obesity is widespread and a serious health concern that is linked to some illnesses, including a higher risk of heart disease, stroke, coronary artery disease, cardiovascular disease, and some forms of cancer. It also significantly raises early mortality and financial expenses.
Statistics
A person who is 20 years of age or older and has a body mass index (BMI) of 30 or higher is considered obese by the CDC, whereas an adult Somebody is regarded as overweight if their body mass index ranges from 25.0 and 29.9.
Adult obesity can be classified into three groups. A BMI of 33 to 35 corresponds to class 1 obesity; a BMI of 32 to 40 is termed class 2 overweight; and a BMI of 42 or higher is divided as class 3 obesity. It can also be described as severe or extreme weight gain (currently referred to as pathological obesity). Since 1960–1962, when 13% of adult Americans were obese, the obesity rate has been rising gradually. According to CDC data from 2014, almost one-third (about 36.5%) of American people.
Epidemiology
A chronic health issue is obesity. It is a major factor that leads to cardiovascular disease and type II diabetes. Cancer (such as colorectal cancer), osteoarthritis, liver disease, sleep apnea, depression, and other illnesses that impact mortality and morbidity are also linked to it.
When considering the long-term effects, adolescents who are overweight have a 70% risk of becoming overweight or obese adults; if one or both parents are overweight or obese, the likelihood rises to 80%.
American Samoa has the highest obesity percentage in the US, with 75% of people there being fat and 95% being overweight.
Prevalence
“The government observed in the report that their declared objective is to lower the percentage of Americans who are overweight or obese: “The increasing incidence of adult obesity in the United States is still higher than the Healthy Americans 2031 target of 34.0%.”
The highest frequency of obesity (43.5%) remains prevalent in those around the ages of 38 and 57. The lowest rates, 34%, were observed beyond individuals aged 24 to 29.
The CDC report also revealed that rates of severe obesity are still rising. The percentage of adults having a BMI of 40 or more rose from 7.7% to 9.4% when age was taken into account.
Causes of obesity
Fast food and energy drinks are common sources of extra fat in the diets of the vast majority of Americans. People who are obese might devour more when they are anxious or nervous, feel thirsty earlier, or need more calories before feeling full. The majority of Americans do not adhere to a healthy dietary pattern, according to the USDA’s Dietary Guidelines for Americans, 2020–2025.
Few people undergoing nutrient testing could meet the requirements without the aid of enrichment or fortification. Americans consume a lot of fast food. Two out of three adults eat fast food at least once a week, and 36.6% of adults eat it on any given day, which is slightly more than one out of three. Even though fast food’s detrimental effects—such as its high-calorie content and lack of nutritional value—are well known, its convenience—particularly its affordability and time-saving nature—keeps it popular.
The amount of food consumed is also a significant factor. According to a study, the amount of food in market products has significantly increased during the 1970s, surpassing the federal dietary guidelines. The growth of the food sector during the 1970s, marketing tactics, and consumer demand are some of the causes of this surge. It has also been noted that the same franchises’ menu items vary greatly in terms of quantity sizes. American food portions can often be up to twice as large as those of their British counterparts.
According to the 2018 Physical Activity Guideline for Individuals, 23.5% of those aged 18 and above in 2020 engaged in cardiac exercise that strengthened their muscles. This indicates that over 75% of the population did not engage in the recommended amount of physical activity for their health. The 20th century saw a rise in the use of cars, which reduced the need for physical activity. As percent 2024, for instance, 91.7% of the American population are drivers.
Effects on life expectancy
One of the main causes of the United States’ comparatively lower life expectancy when compared to other high-income nations is the country’s high obesity rate. Obesity is responsible for 14% of cancer deaths in males and 20% of cancer deaths in women in the United States. Obesity has been attributed to the rise in lifespans observed in the United States over the 19th century.
If obesity rates in younger generations continue to climb, their lifespans and general wellness are going to fall in subsequent generations. Olshansky asserts that fat reduces “the length of life of people who are severely obese by an estimated 5 to 20 years.” History demonstrates that because obesity is more likely to occur in younger generations, the number of years lost will keep increasing.
Obesity in children and adolescents is becoming more prevalent at younger ages. They may not live as long as their parents did because they are eating less healthily and exercising less. Because of obesity and other health hazards later in life, younger generations can anticipate a shorter life expectancy.
Obesity has been associated with an increase in heart attack and stroke, type II diabetes, hypertension, and impairment. More specifically, in the United States, diabetes has become the sixth most common cause of morbidity. According to estimates from the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services in 2008, 23.6 million adults aged 20 and older had diabetes, 90–95% of whom had type 2 diabetes, and 57% of adults were pre-diabetic.
It has also been demonstrated that pregnancy and delivery difficulties are more common in obese women. Compared to kids born to women of normal weight, newborns born to obese women are nearly twice as likely to be stillborn and nearly three times as likely to die within a month of delivery.
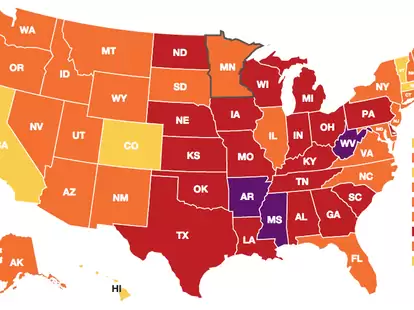
The greatest percentages of obesity have been observed in the Plains region and the southern region.
| Territory | Adult Obesity Rate |
| West Virginia | 41.0% |
| Louisiana | 40.1% |
| Oklahoma | 40.0% |
| Mississippi | 39.5% |
| Tennessee Alabama | 38.9% |
| Ohio | 38.3% |
| Ohio | 38.1% |
| Delaware | 37.9% |
| Indiana | 37.7% |
| Kentucky | 37.7% |
More than one in five American individuals were fat in 2022, with obesity rates exceeding 20% in every state and territory.
Overall, the highest rates of Obesity were seen in the Midwest (35.8%) while in the South (35.6%) nearly the same, followed by the Northeast (30.5%) and West (29.5%).
FAQs
What is the United States’ current obesity rate?
Adult obesity prevalence was 40.3% between August 2021 and August 2023, with no discernible gender differences. Adults aged 40–59 had a higher prevalence of obesity than those aged 20–39 and 60 and more.
In terms of obesity, where does the US stand?
The study found that In 2022, the United States’ adult prevalence of obesity increased from 22.3% in 1990 to 42.6% for women and from 17.4% to 43.1% for men, placing the continent in the tenth place spot in the world for male obesity and 36th for female obesity.
Why is America the obesity leader?
Overeating in food and inadequate physical activity are common contributing factors. A person’s body weight can be decreased by eating healthily, however, the general public frequently makes mistakes about what they should and shouldn’t eat, as well as how much or how little they should consume.
Which state in the US has the greatest percentage of obesity?
The states in the United States with the highest percentages of obese people are West Virginia, Mississippi, and Arkansas. The states with the lowest rates of obesity are the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, the state of Colorado, and Hawaiian.
References
- Tin, A. (2024, September 24). The obesity rate in U.S. adults is no longer growing, new CDC data suggests. CBS News. https://www.cbsnews.com/news/obesity-rate-us-adults-cdc-data-map/#:~:text=Now%20the%20CDC%20estimates%20that,virtually%20every%20year%20since%202011.
- Obesity in the United States. (2024, November 23). In Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Obesity_in_the_United_States
- Holland, K. (2023, March 3). Obesity Facts. Healthline. https://www.healthline.com/health/obesity-facts
- Kekatos, M. (2024, September 24). Obesity prevalence among US adults falls slightly to 40%, remains higher than 10 years ago: CDC. ABC News. https://abcnews.go.com/Health/obesity-prevalence-us-adults-falls-slightly-40-remains/story?id=113927451
- USAFacts. (2023, March 21). US obesity rates have tripled over the last 60 years. USAFacts. https://usafacts.org/articles/obesity-rate-nearly-triples-united-states-over-last-50-years/
- Obesity in the U.S. – Food Research & Action Center. (2024, October 22). Food Research & Action Center. https://frac.org/obesity-health/obesity-u-s-2