Underweight
Introduction
Underweight refers to a condition where a person’s body weight is significantly below the recommended range for their age, sex, and height. It is typically assessed using the Body Mass Index (BMI), where a BMI below 18.5 is considered underweight. This condition can result from various factors, including inadequate caloric intake, medical conditions, or genetic predisposition.
It’s possible that an underweight individual isn’t getting enough nutrition for good skin, strong bones, and hair. Osteoporosis, anemia, fatigue, and other symptoms are related symptoms or indicators.
Doctors can recommend therapies to assist people in acquiring weight, even if some people may be prevented from gaining weight by a medical condition or genetic background.
The reasons, remedies, and when to consult a doctor are all covered in this article on how to tell whether you are underweight.
Underweight: What Is It?
When it comes to trade and finance, underweight describes one of two circumstances. An underweight investment lacks an adequate proportion of a particular investment relative to its weight relative to the fundamental comparison portfolio. The term “underweight” can also describe an analyst’s assessment of a security’s potential underperformance in the future.
How to determine Underweight?
To determine if your weight falls within a healthy or unhealthy range, you can utilize the body mass index or BMI. Body fat can be estimated using BMI. Enter your height and weight into our Centers for Disease Control and Prevention BMI calculator to determine your BMI.
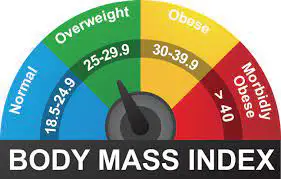
Healthy weight can be measured in several ways, including BMI. Some women weigh less than average, yet it’s still healthy. Discuss with your physician or nurse what your ideal weight is.
Reasons for being Underweight:
An individual may be underweight for several reasons. There may occasionally be a connection between several underlying factors. Among the causes of underweight are:
Family background. Due to physical traits passed down in their family, some persons have a traditionally low BMI.
An elevated metabolism. An individual with a strong metabolism could not put on much weight even if they eat foods that are heavy in calories.
Regular exercise. People who run or participate in other high-intensity physical activities, like athletes, may burn a lot of calories and lose weight.
Physical sickness or long-term condition. Certain disease kinds can make it hard to gain weight since they frequently cause nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. A person may not feel like eating because of several problems that reduce their appetite. Cancer, diabetes, thyroid issues, and digestive diseases like Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis are a few examples.
mental disease. Eating disorders including bulimia and anorexia, obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), depression, and anxiety can all have an impact on a person’s capacity to eat. A person’s appetite and body image may be impacted by any of these diseases.
A physician can assist a patient in determining the reason behind their low BMI and suggest a course of action that will enable them to gain weight healthily.
Why being underweight may cause issues:
Being underweight is bad for your health. It might result in:
Nutritional deficiencies: If you are underweight, you probably don’t eat a balanced, healthful diet, which might cause you to be deficient in nutrients that your body needs to function correctly. For bones to remain solid and in good health, calcium is required. You run the danger of developing osteoporosis, or fragile bone disease, later in life if you don’t receive enough calcium. Anemia, which can leave you feeling exhausted, can occur if you’re not getting enough iron in your diet.
Immune system weakness: Being underweight weakens your immune system, leaving you more vulnerable to colds, the flu, and other ailments.
Fertility issues: underweight women may experience a cessation of menstruation.
Therapy for Underweight:
There are several healthy ways for someone who is underweight to gain weight.
A person might gain weight by adopting a healthful diet that combines nutritious calorie-dense meals. A doctor might advise someone to try a certain diet to gain weight, or they might suggest that they see a nutritionist, who can assist them in creating a diet plan that suits them.
A diet for weight gain may consist of the following essential elements:
Snacks are added. Snacks high in whole-grain carbohydrates and protein can contribute to weight gain. A handful of almonds, pita chips and hummus, trail mix, peanut butter crackers, and protein bars are a few examples.
Consuming several tiny meals every day. A person may occasionally be underweight as a result of their inability to handle substantial meals. Alternatively, a person can have multiple little meals during the day.
The inclusion of other foods. Nut butter on whole-grain bread, sunflower or chia seeds on a salad or soup, or slivered almonds over cereal or yogurt are all examples of how someone can include calorie-dense foods into their current diet.
Steer clear of empty calories. Consuming foods high in calories can lead to weight gain, but they also include excess fat that can harm the heart and blood vessels. Foods that are heavy in salt and sugar should be avoided.
When it is feasible, doctors may also recommend appetite stimulants or antiemetic drugs to help an underweight individual put on weight. These therapies are typically only prescribed by doctors when at-home remedies have failed.
Work out. Because muscle hypertrophy increases body mass, exercise is another way for underweight persons to acquire weight. Exercises including weightlifting are useful for both promoting weight gain and improving muscular tone. It has also been demonstrated that lifting weights increases bone mineral density, which is something that underweight persons are more likely to have insufficiently.
Because exercise is catabolic, it causes a temporary loss of mass. Nevertheless, anabolic overcompensation during recovery leads to muscle growth, increasing total mass. This may occur as a result of increased muscle protein or improved muscle glycogen storage. For someone who is not motivated to eat, exercise might also assist pique their appetite.
The dangers of underweight:
Being underweight does not always have negative consequences or symptoms for those who are underweight. Nonetheless, some underweight persons have the following symptoms:
Osteoporosis. A 2016 study found that underweight women are more likely to develop osteoporosis, a condition in which the bones are fragile and more likely to break.
Issues with the skin, hair, or teeth. If a person does not get enough nutrients from their daily diet, they may show physical symptoms like dry skin, hair loss, thinning skin, or poor dental health.
Becoming ill a lot. A person may not be obtaining enough nutrients to fight against disease if their diet does not provide them with enough energy to maintain a healthy body weight.
Infections. A person may become unwell more frequently as a result, and ordinary illnesses like the common cold may persist longer than they otherwise would.
Experiencing constant fatigue. Fatigue may result from consuming insufficient calories to sustain a healthy weight.
Anemia. Anemia, or low blood counts, is more common among underweight people and can lead to headaches, exhaustion, and dizziness.
irregular times. Adolescents may experience delayed or nonexistent menstruation, underweight women may experience irregular periods, or both. Menstrual irregularities or nonexistence might lead to infertility.
premature births. A woman who is underweight during pregnancy is more likely to experience pre-term labor, which is defined as giving birth before 37 weeks, per a study published in An International Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology.
sluggish or compromised growth. For young individuals to grow and create healthy bones, they require nutrition. A person may not develop normally if they are underweight and not getting enough calories.
In comparison to those with an average BMI, being underweight is linked to a higher risk of death, per a study published in the journal BMC Public Health.
When to consult a physician
If someone has attempted to gain weight but has failed, they should consult their physician. See a doctor if you’re having any health problems, such as irregular periods or infertility, as a result of your inability to gain weight.
A person needs professional help when they suffer from a disorder of appetite or a mental disease. Regretfully, people might not always be aware that their actions are problematic.
Signs of eating disorders:
- covert actions
- abrupt and inexplicable weight reduction
- refusal to attend family or social events
- looking worn out
- avoid eating in front of other people
Friends and relatives should advise someone who exhibits these symptoms to consult a doctor or therapist for professional assistance.
Summary
Underweight individuals may be more susceptible to complications, such as issues with their teeth, bones, and fertility.
A healthy BMI should be the goal of every individual. A person can attain and maintain a healthy weight by working with a medical practitioner.
FAQs
What occurs when someone is underweight?
You may experience frequent illness or extreme fatigue if you are underweight. That can be the result of your diet not providing you with the proper nutrients. Additionally, you can notice that your teeth are impacted, your skin becomes extremely dry, and your hair becomes thinner or falls out.
How can I determine whether I’m underweight?
A satisfactory weight is defined as having a BMI that is beneath the 85th percentage mark for height, age, and gender, but equal to or higher than the 5th percentile.
What has caused me to lose weight?
There are numerous reasons why people lose weight without intending to. A stressful event like a divorce, losing one’s career, or losing a loved one could be the cause. Malnutrition, a medical ailment, or a combination of these may be the cause.
In kilograms, what is a slim weight?
If a person weighs 98 kg, they are considered fat, and if they weigh less than 63 kg, they are considered slim. Length: 1.84 The ideal weight is between 67 and 84 kg. When a person weighs 101 kg, they are described as fat, and when they weigh less than 64 kg, they are described as slim.
What is the calorie-dense food?
Dairy Products with Full Fat: Breakfast items abundant in calories, protein, and vital vitamins and minerals include whole milk, yogurt, paneer, and cheese.
References
- Crna, R. N. M. (2023, July 27). What are the risks of being underweight? https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/321612#outlook
- Chen, J. (2022, September 27). Underweight: What it Means, How it Works, Example. Investopedia. https://www.investopedia.com/terms/u/underweight.asp
- Family Information Service | Underweight adults. (n.d.). Family Information Service. https://fisd.oxfordshire.gov.uk/kb5/oxfordshire/directory/advice.page?id=LYA723-4XLM
- Wikipedia contributors. (2024, December 20). Underweight. Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Underweight
- Underweight | Office on Women’s Health. (n.d.). OASH | Office on Women’s Health. https://womenshealth.gov/healthy-weight/underweight






One Comment